
Calcite
Practical significance
Calcite is considered to be particularly important for its link with climate evolution and water resources on Mars. Moreover, calcite is also found in the Earth's atmosphere.
Main constituent
Calcite
Color
White powder
Particle size Mie: reff (μm)
3.3
Particle size Mie: veff
4.9
Particle size Fraunhofer: reff (μm)
1.7
Particle size Fraunhofer: veff
7.6
Size distribution plot:
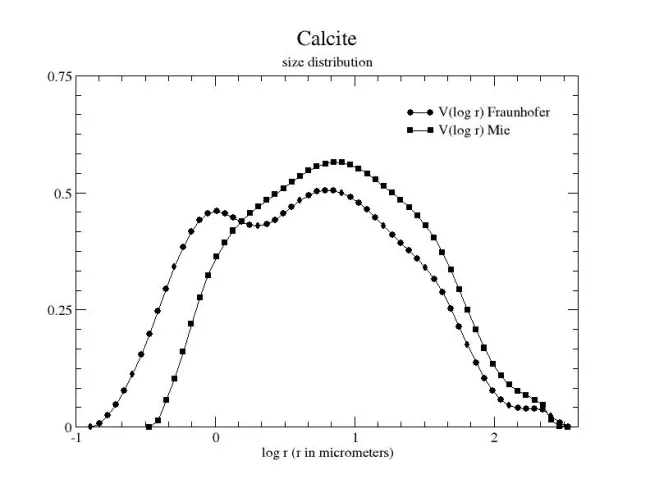
Size distribution table
SEM/TEM images:
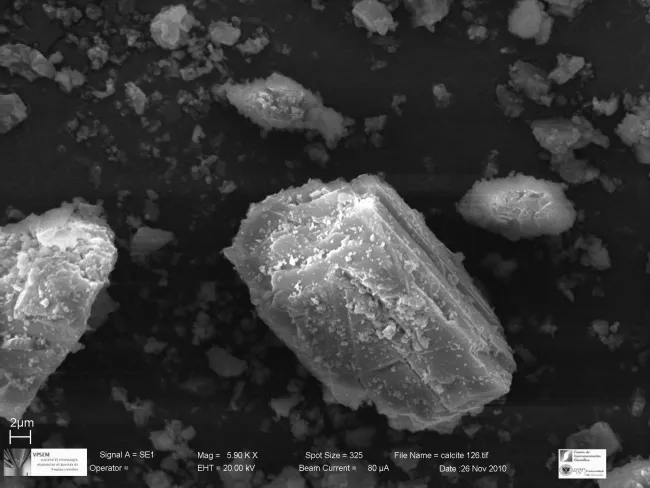
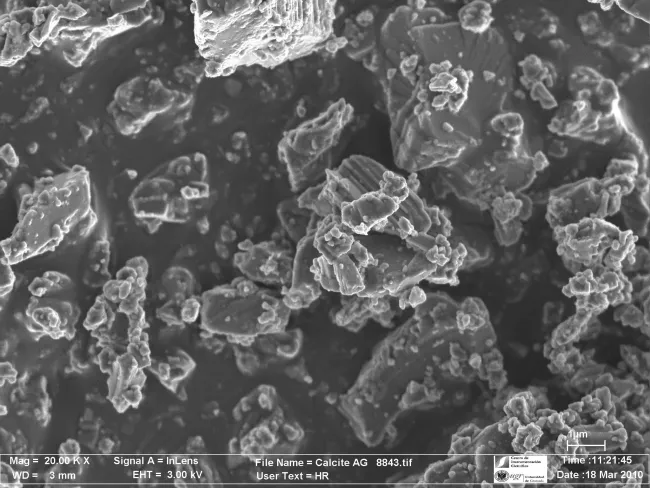

All SEM/TEM images (zip file)
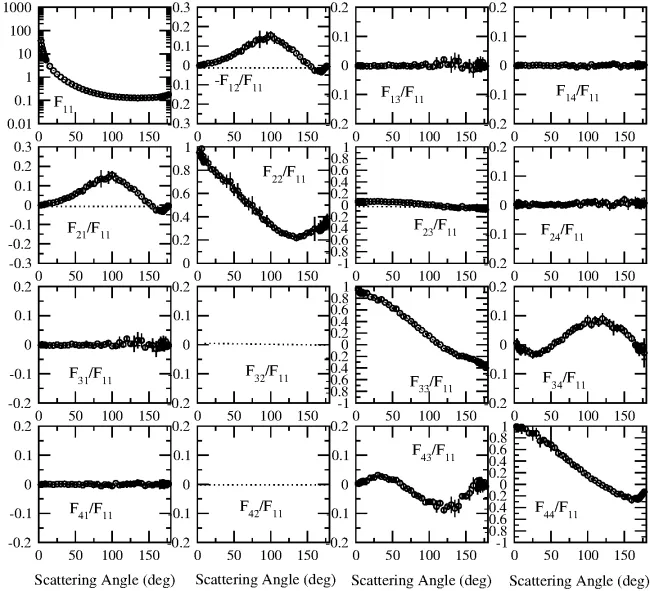
Scattering matrix (1) wavelength in nm
647.00 nm
Scattering matrix (1) table
Scattering matrix (1) plot:
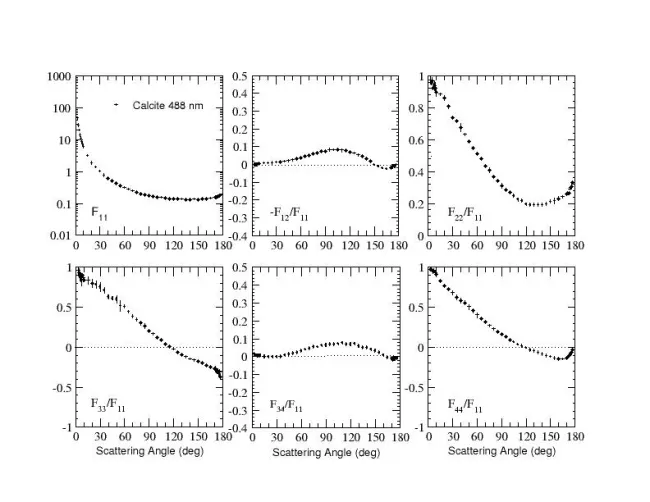
Scattering matrix (2) wavelength in nm
488.00 nm
Scattering matrix (2) table
Scattering matrix (2) plot:
Synthetic scattering matrix (1) wavelength in nm
488.00 nm
Synthetic scattering matrix (1) table M
Synthetic scattering matrix (1) table F
Synthetic scattering matrix (2) wavelength in nm
647.00 nm
Synthetic scattering matrix (2) table M
Synthetic scattering matrix (2) table F
Refractive index
Calcite is a uni-axial birefringent material, so it has one optic axis and, instead of one refractive index, it has a dielectric tensor specified by two principal dielectric functions, the ordinary (mo) and the extraordinary (me) refractive indices. At 647 nm no=1.655 and ne=1.485. The imaginary part is assumed to be zero (Gosh 1999).
Angle range (deg)
[3,177]
Reference/s