
Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbon (HAC)
Practical significance
HAC is considered to be a realistic carbonaceous interstellar dust analog.
Origin
HAC analogues generated at the Cold Plasma Laboratory at the Instituto de Estructura de la Materia (IEE-CSIC), consisting of a low-pressure plasma reactor where analogs of cosmic dust grains are produced under controlled conditions and the gas-to-particle conversion processes can be analyzed in situ (Jiménez-Redondo et al. 2019).
Main constituent
hydrogenated amorphous carbon
Cosmic analogs density
porous
Particle size Mie: reff (μm)
5.0
Particle size Mie: veff
2.3
Particle size
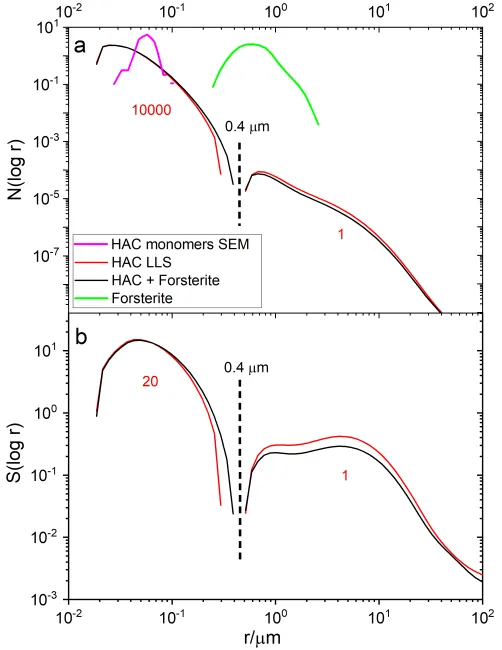
Normalized logarithmic-scale number PSD N(log r) of monomers and aggregate particles of HAC and forsterite. The numbers under the curves indicate the relative contribution to the number of particles and surface for r < 0.4 μm and r > 0.4 μm.
Size distribution plot:
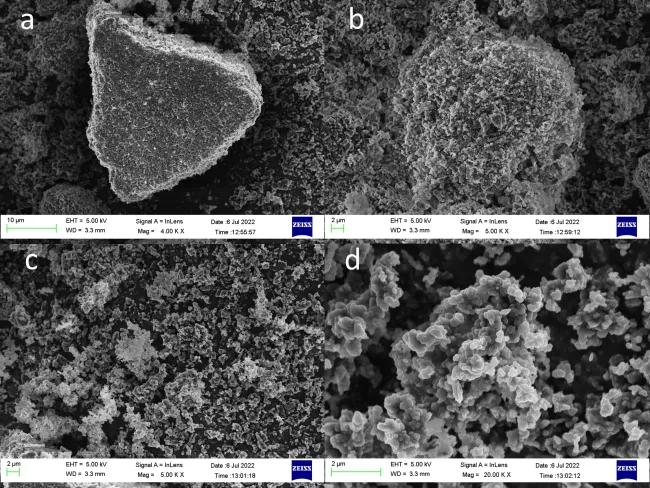
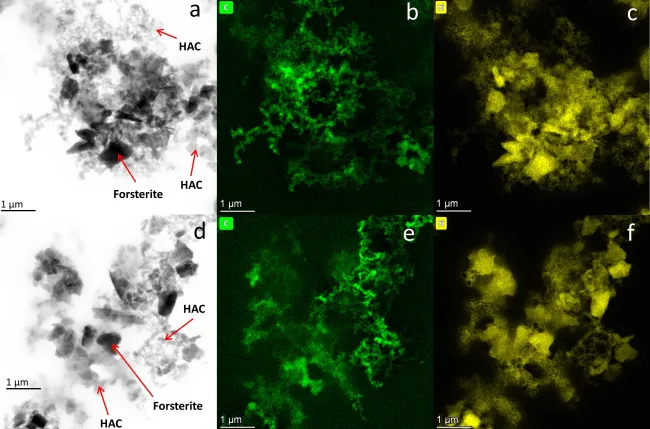
SEM/TEM images:

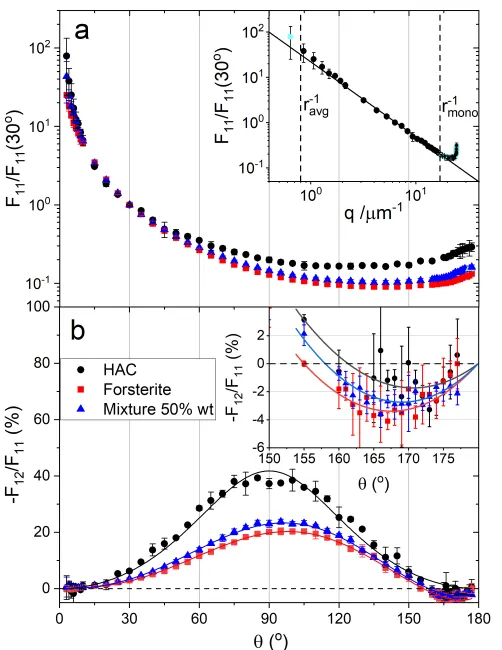
Scattering matrix (1) plot:
Refractive index
m(514 nm) = 1.7 + i0.015
Complex refractive indices
Angle range (deg)
[3,177]
Reference/s